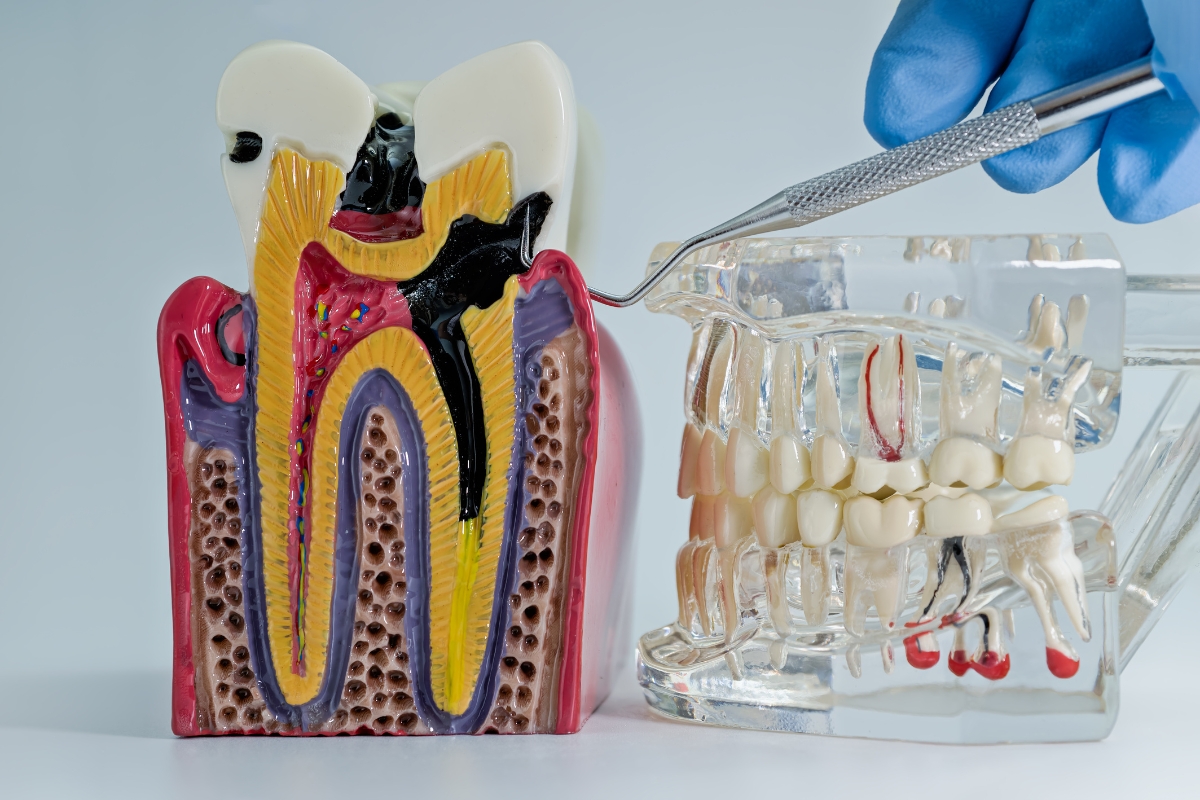
Tooth infections, such as dental abscesses and pulpitis, can have serious implications. These infections occur when bacteria invade the tooth or surrounding tissues. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial for preventing complications. Ignoring an infection can lead to its spread to other parts of the body, which poses significant health risks.
This blog will discuss the nature of tooth infections, their common causes, and how they develop. It will highlight the localized and systemic symptoms to watch for. Furthermore, it will explore indications that a tooth infection may extend to the body. Lastly, it will cover the risks of untreated infections, when to seek medical help, and preventive measures to maintain oral health.
What is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection occurs when bacteria infiltrate the tooth or surrounding tissues. If untreated, this can lead to inflammation, pain, and further complications. The most common types include dental abscesses and pulpitis. A dental abscess forms when pus accumulates due to bacterial infection. Pulpitis is the inflammation of the tooth’s pulp, usually from decay.
Several factors contribute to tooth infections. Cavities are one of the primary causes, as they create openings for bacteria. Gum disease, or periodontal disease, can also lead to infections. Trauma to the tooth, such as a crack or fracture, provides an entry point for bacteria.
Infections develop when bacteria multiply within the tooth or surrounding tissues. This can lead to inflammation and pus formation. If the infection is not addressed, it can spread to the jawbone or other body areas, causing severe complications.
Signs and Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Localized Symptoms:
- Pain and Sensitivity: You may experience severe toothache, especially when chewing or exposing the tooth to hot or cold temperatures. This discomfort often indicates an underlying infection.
- Swelling and Redness in the Gums: Infected gums can appear swollen and inflamed. You might notice redness around the affected tooth, indicating an immune response to infection.
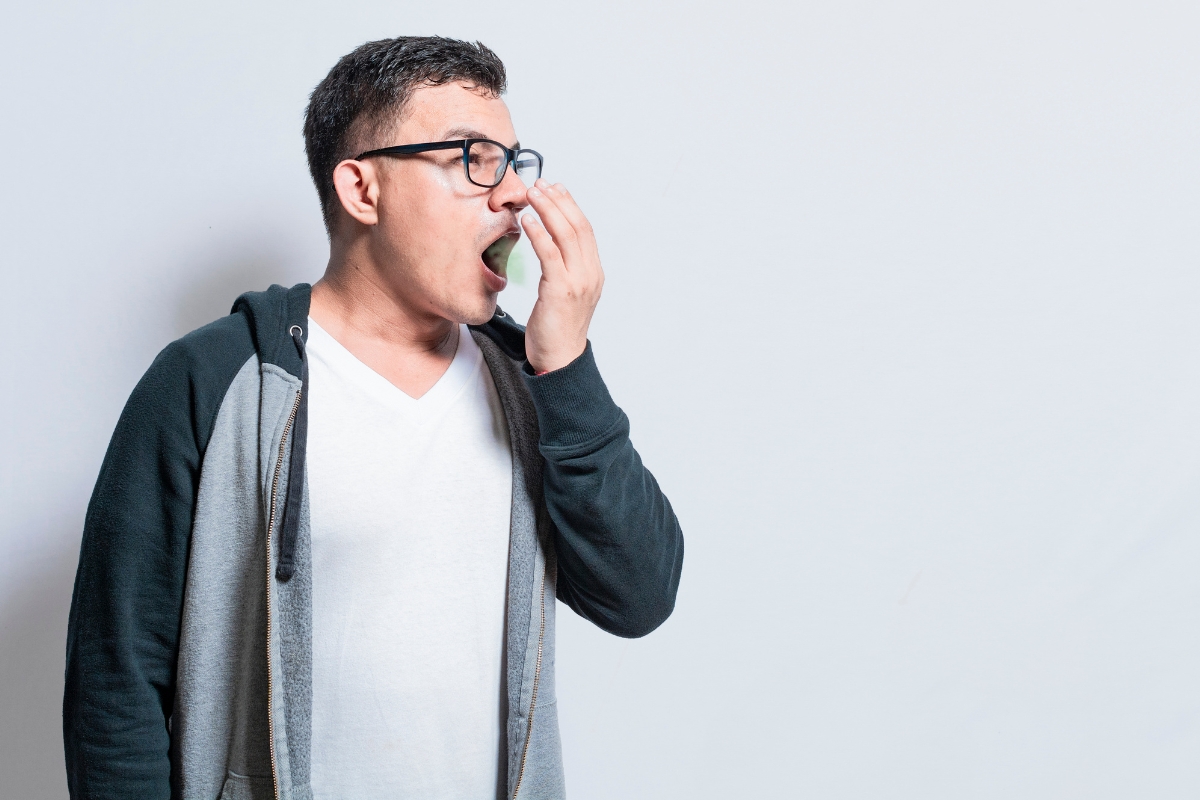
- Bad Breath or Unpleasant Taste: An infection may cause persistent bad breath or a foul taste in your mouth. This occurs due to pus and bacteria accumulation.
Systemic Symptoms Indicating Potential Spread:
- Fever and Chills: A systemic infection can trigger a fever, which indicates that the body is fighting off the infection. Chills often accompany fever.
- Fatigue and Malaise: As your body battles the infection, you may feel unusually tired and weak. This fatigue can be debilitating and affect daily activities.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Infections can cause your neck or jaw lymph nodes to swell. This is a sign your body is reacting to infection.
Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for effective treatment. Delaying medical care can lead to more serious complications.
Indications of a Tooth Infection Extending to the Body
Respiratory Issues:
If you experience shortness of breath or a persistent cough, these may be signs of a serious complication. Infections can spread to the lungs, causing respiratory distress.
Cardiovascular Symptoms:
Tooth infections can lead to heart infections, such as endocarditis. Symptoms include chest pain and irregular heartbeat. If you notice these signs, seek immediate medical attention.
Digestive Symptoms:
Nausea and vomiting can occur as a response to an infection spreading through the bloodstream. Diarrhea may also happen as your body tries to rid itself of toxins.
Neurological Symptoms:
In rare cases, infections can affect your nervous system. Symptoms like confusion or severe headaches may arise. Signs of meningitis, such as a stiff neck and sensitivity to light, require immediate evaluation.
These indications highlight the seriousness of a tooth infection. If you notice any of these symptoms, do not ignore them. Prompt medical intervention can prevent serious health issues.
Risks Associated with Untreated Tooth Infections
Untreated tooth infections pose severe risks to your overall health. One of the most serious complications is sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by the body's extreme response to infection. Sepsis can lead to organ failure and requires immediate treatment.
Another potential complication is osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone. This condition can develop if the infection spreads to the jawbone, causing severe pain and requiring surgical intervention.
Ignoring a tooth infection can impact your oral health and your overall well-being. Infections can spread through the bloodstream, affecting other organs and systems in the body. This underscores the importance of seeking timely dental treatment.
Regular dental check-ups can help identify and treat infections early, minimizing the risk of complications. Prioritizing your dental health is essential for maintaining overall health.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
If you notice signs of a tooth infection, seek medical attention promptly. Signs that warrant immediate care include severe pain, facial or mouth swelling, and fever. You should also seek help if you experience difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Consult your dentist if you suspect a tooth infection. They can assess your condition and recommend appropriate treatment. Sometimes, your dentist may refer you to a physician or an oral surgeon for further evaluation.
Ignoring symptoms can lead to serious complications, so do not hesitate to seek help. Timely intervention can make a significant difference in your recovery and overall health.
Preventive Measures
Maintaining good oral hygiene is vital for preventing tooth infections. Brush your teeth at least twice daily and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to help reduce harmful bacteria.
Regular dental check-ups are essential. Your dentist can identify early signs of decay or gum disease before they lead to infections. Schedule visits every six months or as recommended.
Lifestyle factors also affect oral health. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals strengthens teeth and gums. Avoid excessive sugary foods and drinks that promote tooth decay. If you smoke, consider quitting, as smoking increases the risk of gum disease and tooth infections.
Early detection of tooth infections is crucial for preventing serious complications. Recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment can protect your health. Remember to prioritize your oral hygiene and maintain regular dental visits.
Take action now! If you experience any symptoms of a tooth infection, schedule a dental check-up. Your health depends on it, so do not wait until it is too late.